Type Coverage
Source code: github.com/pestphp/pest-plugin-type-coverage
Type Coverage is a metric used to measure the percentage of code that is covered by type declarations. This can help developers identify parts of their code that may not be fully typed, indicating a potential risk for bugs and other issues.
To start using Pest's Type Coverage plugin, you need to require the plugin via Composer.
1composer require pestphp/pest-plugin-type-coverage --devAfter requiring the plugin, you may utilize the --type-coverage option to generate a report of your type coverage.
1./vendor/bin/pest --type-coverageUnlike code coverage, type coverage does not require you to write any tests. Instead, it analyzes your codebase and generates a report of your type coverage. This report will display a list of files and their corresponding type coverage results.
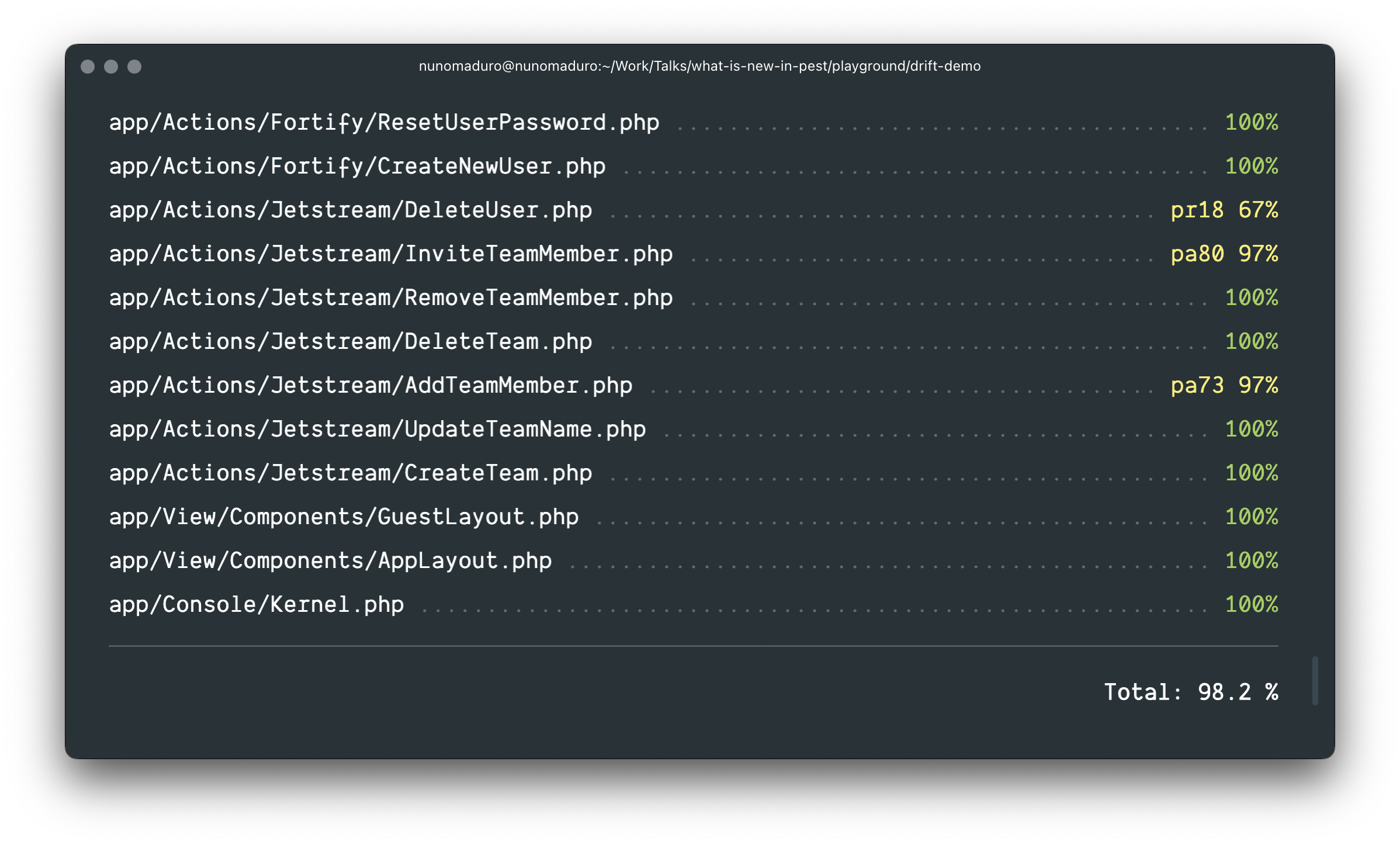
If any of your files are missing type declarations, they will be highlighted in yellow and displayed using their respective line numbers, and type of declaration that is missing.
As example, rt31 means that the return type of the function on line 31 is missing. On the other hand, pa31 means that the parameter type of the function on line 31 is missing.
Ignoring Errors
Sometimes, you may want to ignore a specific error or line of code. To do so, you may use the @pest-ignore-type annotation:
1 protected $except = [ // @pest-ignore-type2 // ...3 ];4}Compact Output
Often, when checking type coverage, you only want to see files that do not currently have 100% type coverage. To do this, you can use the --compact option:
1./vendor/bin/pest --type-coverage --compactMinimum Threshold Enforcement
Just like code coverage, type coverage can also be enforced. To ensure any code that is added to your application is fully typed, you can use the --type-coverage and --min options to define the minimum threshold values for type coverage results. If the specified thresholds are not met, Pest will report a failure.
1./vendor/bin/pest --type-coverage --min=100Different Formats
In addition, Pest supports reporting the type coverage to a specific file:
1./vendor/bin/pest --type-coverage --min=100 --type-coverage-json=my-report.jsonIn this chapter, we have discussed Pest's Type Coverage plugin and how it can be used to measure the percentage of code that is covered by type declarations. In the following chapter, we explain how can you mutation testing to improve the quality of your tests: Mutation Testing →